The question of who was the first person on Earth is one of the most interesting mysteries ever. We’ve all asked this question at least once, whether while awake or dreaming.
Yet, do we have an answer? Can we even find an answer? Is answer possible from any kind of scientific perspective?
Let’s explore.
Related:
Different Approaches to the First Person on Earth?
From a scientific perspective, there was no “first human” on Earth. Evolution doesn’t work like flipping a switch—it’s a gradual, continuous process over millions of years. Instead of one individual suddenly being “human,” populations of our ancestors slowly acquired traits that define us today, such as larger brains, complex language, and advanced tool use.
Namely, the first humans are believed to have evolved from earlier hominids such as Homo erectus, a species that lived between 1.9 million and 70,000 years ago.
However, the distinction between Homo erectus and Homo sapiens, the species to which modern humans belong, is not exactly clear-cut.
Additionally, one of the most famous fossils of a human ancestor is Lucy, a 3.2-million-year-old skeleton discovered in Ethiopia in 1974. Lucy is believed to belong to the species Australopithecus afarensis, which is not a direct ancestor of Homo sapiens but somewhat a close relative.
Namely, Lucy has been formally categorized as a hominid, representing a precursor to humanity. Her species eventually gave rise to Homo habilis, then followed by Homo erectus, and ultimately concluded with us – Homo sapiens.
Recommendation: If you'd like to read THE ONE book on human evolution and learn everything about Lucy and our beginnings, we highly recommend the following: 'Lucy: The Beginnings of Humankind.' Written by the man who found Lucy - Donald Johanson!
While Lucy provides valuable insights into the evolution of humans, she is certainly not the first person on Earth.
Besides that, religious and mythological views on the first humans differ greatly from scientific perspectives.
For example, many cultures have creation myths that describe the origin of humans as a divine act of a god or gods. These myths often involve a first human or pair of humans who are created by a deity. While these myths are not scientific nor evolutionary, they do provide some insight into the cultural and historical context in which they were created.
And so, let’s first start with the evolutionary and scientific view going back to the first primates.
Interesting fact: As much as 2% of the DNA of people with European or Asian roots comes from Neanderthals.
Evolution of Primates – 10 Events in Human Evolution

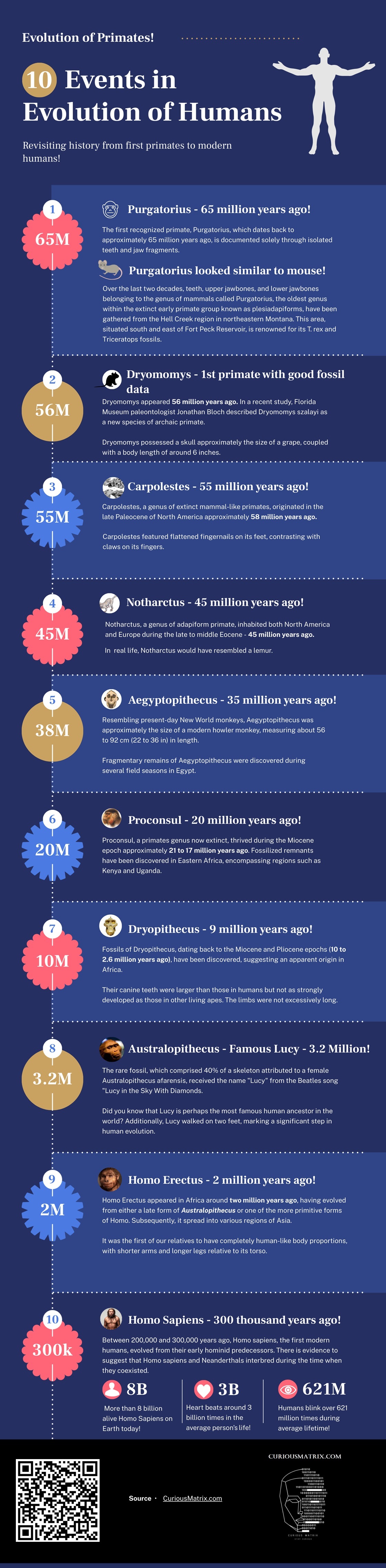
From the evolution perspective, the history of primates spans for millions of years. As far as we know, the journey begins with the Dryomomys, a small, tree-dwelling creature that marked the early steps in the development of primates.
Around 55 million years ago, Carpolestes emerged, exhibiting adaptations that allowed them to navigate both trees and the ground. This remarkable creature paved the way for the subsequent diversification of primates.
For example, Notharctus, with its lemur-like appearance, appeared around 45 million years ago, further contributing to the evolution of primates
Then Around 38 million years ago, the forests of ancient Egypt were home to Aegyptopithecus, an early catarrhine primate. This marked a crucial point in primate evolution as catarrhines would later give rise to Old World monkeys and apes, including humans.
Then the Proconsuls emerged around 20 million years ago. This ape-like creature inhabited the dense forests of Africa and is considered a potential common ancestor of both humans and modern apes. Proconsul showcased primitive ape characteristics, setting the stage for further evolutionary developments.
Approximately 10 million years ago, Dryopithecus entered the scene. This ape, which lived in Europe and Africa, shares common ancestry with modern orangutans, adding another branch to the primate family tree.
Around 4 million years ago, Australopithecus (the famous Lucy) walked the Earth, marking a pivotal moment in human evolution. This hominid genus displayed a combination of ape and human features
The evolution continued with Homo erectus, appearing around 2 million years ago. This species demonstrated advanced tool use, control of fire, and the ability to adapt to diverse environments. Homo erectus paved the way for Homo sapiens, our species, which emerged around 300,000 years ago.
Between those occurrences, numerous other species emerged. However, in our perspective, these events encapsulate the top 10 milestones in human or primate history.
And so, for easier reading we prepared comprehensive infographics visually describing those events.
Interesting fact: The name "Lucy" comes from the Beatles' song "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds," which played during the fossil’s discovery party.
Human Evolution Infographics
10 Events in Evolution of Primates
Click here (or on image) for enlarged version.
Scientific Perspective

Evolutionary Biology
As mentioned, according to evolutionary biology, humans did not simply appear on Earth as fully-formed beings. Instead, they evolved over millions of years from simpler organisms. The first human-like species, known as Homo erectus, appeared around 2 million years ago.
Then Homo erectus eventually gave rise to Homo sapiens, which is the species to which we (modern humans) belong.
Interesting fact: A teenage girl found in Siberia was half Neanderthal and half Denisovan, proving these groups not only met—they had children together.
Genetic Evidence
Genetic evidence additionally suggests that all humans alive today share a common ancestor who lived in Africa around 200,000 years ago.
This ancestor is believed to be the first member of the species Homo sapiens.
However, we must understand that the concept of a “first person on Earth” is not a scientific one. It can’t be.
Namely, evolution is a gradual process that occurs over long periods of time, and there is no clear point at which a new species can be said to have “appeared.”
While looking at it from a certain viewpoint, we might consider Lucy as the first person on Earth, given that her remains are the oldest ones we’ve discovered. However, it’s crucial to note that Lucy belonged to a species other than Homo sapiens.
Moreover, there were undoubtedly other hominids existing at the time, but we have not yet uncovered their skeletal remains.
So in that case, we need to explore religious views.
Religious Perspective

Many religions have their own creation stories that explain how humans came to be on Earth. For example, in Christianity, the first humans were Adam and Eve, who were created by God. In Hinduism, the first humans were Manu and Shatarupa, who were created by the god Brahma.
And, while these stories are important to the religious beliefs of many people, they are certainly not scientific explanations and should not be treated as such.
Nonetheless, let’s explore more about different religious myths and beliefs.
Religious and Mythological Views

Creation Myths
Many religions and mythologies have creation stories that attempt to explain the origin of the universe and humanity. As mentioned, in Hindu mythology, the first humans were created by Brahma, the creator god, who created man as the first of the animals and the strongest
In Christianity, Judaism, and Islam, the first humans were Adam and Eve, who were created by God in the Garden of Eden.
Interesting fact: Some legends, like those in Norse mythology, suggest the first humans were created from trees: Ask and Embla.
Adam and Eve Narrative
According to the Bible, Adam was the first human created by God. God formed Adam from the dust of the ground and breathed life into him, making him a living being. In the Adam and Eve narrative, Eve was created from one of Adam’s ribs, and together they were the first humans on Earth.
According to the Bible, Adam was the first human created by God. God formed Adam from the dust of the ground and breathed life into him, making him a living being. In the Adam and Eve narrative, Eve was created from one of Adam’s ribs, and together they were the first humans on Earth. They lived in the Garden of Eden, a paradise filled with abundant food and no suffering.
God gave them the freedom to eat from any tree except the Tree of the Knowledge of Good and Evil, warning that disobedience would lead to death. Tempted by a serpent, Eve ate the forbidden fruit and shared it with Adam, leading to their expulsion from Eden.
This act, known as the Fall of Man, introduced sin and mortality into the world. However, despite their disobedience, Adam and Eve became the ancestors of humanity.
Culture, Writings, and First Person on Earth?

The question of who was the first person on Earth has also been a source of big interest for writers, researchers, philosophers, and culturists.
So let’s see if we can find some clues (or entertainment) in many different writings throughout history.
Interesting fact: The oldest known drawing, a series of lines in a South African cave, is 73,000 years old.
Literature and Art

The concept of the first person on Earth has been explored across countless writings, reflecting diverse cultural, religious, and philosophical perspectives.
Of course, the biblical account of Adam and Eve, found in the Book of Genesis, remains one of the most well-known narratives, inspiring theological discourse and thousands of literary adaptations. In John Milton’s Paradise Lost, Adam is depicted as a noble and introspective figure, grappling with the weight of free will and the consequences of the Fall.
Ancient Mesopotamian texts, such as the Epic of Gilgamesh, also present a different perspective on humanity’s origins, with the wild man Enkidu emerging as a primordial figure who represents the untamed and natural side of humanity. His transformation through contact with civilization mirrors early human development.
Similarly, in Ovid’s Metamorphoses, the Roman poet describes how the first humans were shaped during the Age of Gold, a peaceful and idyllic period before the corruption of later eras.
Then we also have many philosophical writings. For example, those of the ancient Greeks often approached the idea of the first person as a metaphor for the birth of reason and consciousness.
Plato’s Protagoras explores the myth of Prometheus and Epimetheus, emphasizing the role of intelligence and technology in humanity’s survival.
Hesiod’s Works and Days also reflects on the successive ages of mankind, tracing humanity’s decline from divine creation to mortal struggle.
In Chinese classical texts, the first person is often linked to cosmic forces, as seen in the tale of Pangu, who emerged from a cosmic egg to shape the Earth and heavens. Early Taoist writings suggest that humanity arises naturally from the Tao, reflecting harmony with the rhythms of the universe.
Native American oral traditions similarly describe the first people as emerging from the earth or descending from the sky, reinforcing the deep bond between humanity and nature.
Medieval and Renaissance literature often reimagined the first person through allegory and symbolism. Dante’s Divine Comedy touches on Adam’s role as the progenitor of sin, while also envisioning his redemption through divine grace.
The Romantic poets, such as William Blake, used the figure of Adam to explore themes of innocence, experience, and the eternal struggle for self-awareness.
And so, of course, these are merely different texts and works of imaginative literature (in most cases), but they can serve as a baseline for exploring clues about who the first person on Earth might have been.
Therefore, let’s look at couple of other theories and models.
Scientific Debates & Africa

Out of Africa Theory
The Out of Africa theory, also known as the replacement model, suggests that Homo sapiens evolved in Africa and then migrated to other parts of the world, replacing other hominid species such as Homo erectus.
According to this theory, the first humans appeared in Africa around 300,000 years ago and then spread to other parts of the world around 70,000-100,000 years ago.
Multiregional Hypothesis
The Multiregional Hypothesis, on the other hand, suggests that Homo sapiens evolved independently in different regions of the world from local hominid populations such as Homo erectus. According to this theory, the first humans appeared in different parts of the world at different times and then interbred with each other, resulting in the modern human population
However, both theories have their own limitations and controversies. The Out of Africa theory is supported by genetic evidence, but it does not explain the existence of other hominid species such as Homo erectus. The Multiregional Hypothesis, on the other hand, is supported by fossil evidence, but it does not explain the genetic similarities between different human populations.
From an evolutionary perspective, Homo erectus was a distinct species from Homo sapiens. Homo erectus was the first hominid species to migrate out of Africa and colonize other parts of the world. Homo sapiens, on the other hand, evolved in Africa and then migrated to other parts of the world, replacing Homo erectus and other hominid species
In conclusion, it is impossible to know who was the first person on Earth because of the complexity of human evolution and the different beliefs and perspectives of different religions.
So if we can’t find answers in religion or science, can we perhaps find answers in technology?
Technology and First Person on Earth

As technology has advanced, scientists have been able to learn more about the origins of humanity. One major breakthrough has been in the field of DNA sequencing. By analyzing the genetic material of modern humans and comparing it to ancient DNA samples, scientists have been able to learn more about the genetic history of our species.
Paleogenomics
Another major advance has been in the field of paleogenomics, the study of ancient DNA. By extracting DNA from fossils and other ancient remains, scientists have been able to learn more about the genetic history of our species.
For example, the discovery of the aforementioned 3.2 million-year-old fossil skeleton of a human ancestor known as Lucy has allowed scientists to learn more about the evolution of bipedalism, or walking on two legs.
But still, Lucy hasn’t given us a complete answer.
Interesting fact: Some scientists think that, in the far future, they might use AI to recreate digital models of early humans using DNA from fossils.
Conclusion – Who Was The First Person on Earth?

In conclusion, identifying the initial person on Earth remains mission impossible. Despite possessing archaeological clues and referencing various religious texts, none of these sources offer any kind of conclusive answer.
The theory of evolution challenges the idea of a singular ‘first person,’ asserting that multiple species evolved into humans simultaneously over an extended period. In contrast, religious beliefs claim that Adam was the first man and, consequently, the first person on Earth.
And so, as we struggle with ambiguity in attempting to answer this question, we could perhaps offer three different speculative answers:
- Humans share a common ape ancestor with chimpanzees and perhaps somehow the first person suddenly evolved.
- Gods created first person.
- The first person was created by computer simulation.
While all three points sound rather weird and a product of imagination, we really have no clue. And perhaps at some point in the future with the help of ultra-advanced technology and all-knowing artificial intelligence, we’ll find the final answer.
Consequently, we need to wrap this up with some frequently asked questions about this intriguing topic.
Because at the end of the day we can only ask questions and wonder about this topic. We have some clues, we have some answers.
And perhaps it is best to leave it that way. If we were to truly discover that there was a first person on Earth who was neither created by God nor the product of evolution, we might find ourselves in a strange situation—one that could disrupt our entire way of thinking about the world and the origins of everything.
Frequently Asked Questions

Who was the first modern human?
The earliest Homo sapiens fossils are about 300,000 years old and were found in Morocco.
Who was Lucy?
Lucy was a 3.2-million-year-old hominid, an early ancestor who walked upright but was not yet human.
What did early humans look like?
Early humans in Africa had dark skin, strong features, and body shapes adapted to heat.
Who is the first human in religion?
In the Bible, it’s Adam. In Hinduism, it’s Manu. In Islam, Adam is also the first prophet.
Could AI someday solve the mystery?
Possibly. Advances in DNA analysis and artificial intelligence might reveal secrets we can’t yet imagine.
Did early humans live alongside dinosaurs?
No. Dinosaurs went extinct about 65 million years ago, while humans appeared much later. The closest humans ever got to dinosaurs is through their distant descendants—birds.
How did early humans survive?
They hunted animals, gathered wild plants, used fire, made stone tools, and lived in small social groups. Cooperation was key to survival.
When did humans first use fire?
Evidence suggests humans began using fire at least 1 million years ago. It helped with cooking, warmth, protection, and community bonding.
Were there other human species before us?
Yes. Species like Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo floresiensis, Homo naledi, and Neanderthals all lived before or alongside early Homo sapiens.
Why did Homo sapiens survive when others didn’t?
Scientists believe we had advantages in language, adaptability, and possibly social cooperation. We also interbred with some species, but others eventually disappeared.
Are there still human fossils yet to be discovered?
Absolutely. Many regions remain unexplored or under-excavated. New fossils are found every year that reshape our understanding of human evolution.
Is it possible that humans originated outside of Africa?
While the Out of Africa theory remains the most supported by genetics, some researchers continue exploring alternative models, including the possibility of limited regional evolution.
How do scientists date ancient fossils?
They use methods like radiocarbon dating, stratigraphy (layer analysis), and potassium-argon dating to determine a fossil’s age.
How smart were early humans?
Early Homo sapiens had brains nearly the same size as ours. They created tools, art, and even burial rituals—indicating symbolic thinking and complex social behavior.