
Math is actually extremely interesting and fun, but not in the way it’s presented to us in school. From the very beginning of our formal education days many people unfortunately develop an aversion to mathematics.
But it should not be like that.
Namely, mathematics has been an essential part of human history, and its impact on society is incalculable (pun intended).
From ancient times to the present day, mathematicians have made huge contributions to the field, creating the path for modern science and technology.
Without math, we wouldn’t have computers and we probably wouldn’t be reading (or writing) this article.
Basically, without math, we would probably be living like people 500 or even 1000 years ago.
And so, we wanted to dedicate a special article for special people – genius mathematicians.
In this article, we will be discussing the top 10 greatest mathematicians of all time.
Interesting fact: The word "mathematics" comes from the Greek word "mathema," which means "knowledge" or "learning."
Euclid: The Father of Geometry

Euclid was a Greek mathematician who lived around 300 BCE and is widely regarded as the father of geometry. He authored the book “Elements,” which is considered one of the most influential works in the history of mathematics.
In “Elements,” Euclid presented a systematic approach to geometry, starting with a set of axioms and building upon them to prove various geometric theorems. His work laid the foundation for the study of geometry for centuries to come.
Euclid’s contributions to mathematics extend beyond geometry.
He also made important contributions to number theory, such as his famous proof that there are infinitely many prime numbers.
Interesting fact: Euclid's "Elements" was used as a textbook for over 2,000 years and was second only to the Bible in terms of the number of editions printed.
Archimedes: The Mathematician of Classical Antiquity

Archimedes, born in 287 BC in Syracuse, Sicily, was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer. He is considered one of the most prominent mathematicians of classical antiquity.
Archimedes made huge contributions to mathematics, including the discovery of the principles of buoyancy and the formula for the volume of a sphere.
Archimedes was also known for his work in geometry, where he developed methods to calculate areas and volumes of irregular shapes.
In addition to his mathematical contributions, Archimedes was also an inventor.
He developed machines such as the Archimedes screw, which is still used today to move water from low-lying areas to higher ground.
Interesting fact: Archimedes is said to have discovered the principle of buoyancy while taking a bath, and he was so excited about his discovery that he ran naked through the streets shouting "Eureka!" (meaning "I have found it" in Greek).
Isaac Newton: The Man Who Defined Physics and Mathematics
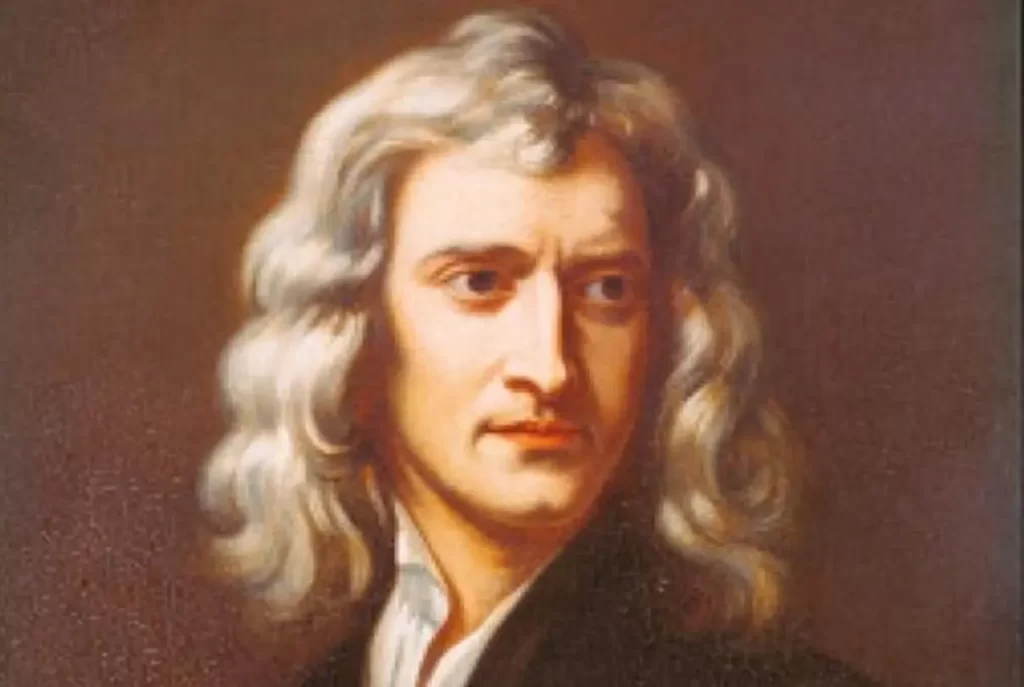

Isaac Newton is commonly regarded as one of the most influential scientists and mathematicians of all time. He is best known for his laws of motion and universal gravitation, which laid the foundation for modern physics.
In addition to his work in physics, Newton also made very important contributions to mathematics.
He developed calculus independently of fellow mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, and his notation and methods are still used today.
He also made important discoveries in the field of optics, including the fact that white light is composed of different colors.
Born in 1642 in England, Newton showed an early talent for mathematics and science.
He attended Trinity College, Cambridge, where he studied mathematics and physics. After graduation, he returned to Cambridge as a professor, where he continued his research and made many of his most important discoveries.
Newton’s most famous work, “Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica” (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), was published in 1687.
In it, he laid out his laws of motion and universal gravitation, which explained how objects move and interact with each other. This work revolutionized the field of physics & mathematics and established Newton as one of the most important scientists of all time.
Interesting fact: Newton was also a devout Christian and spent much of his time studying the Bible and theology. He believed that his scientific discoveries were evidence of God's existence and the beauty of His creation.
Leonhard Euler: The Prolific Swiss Mathematician
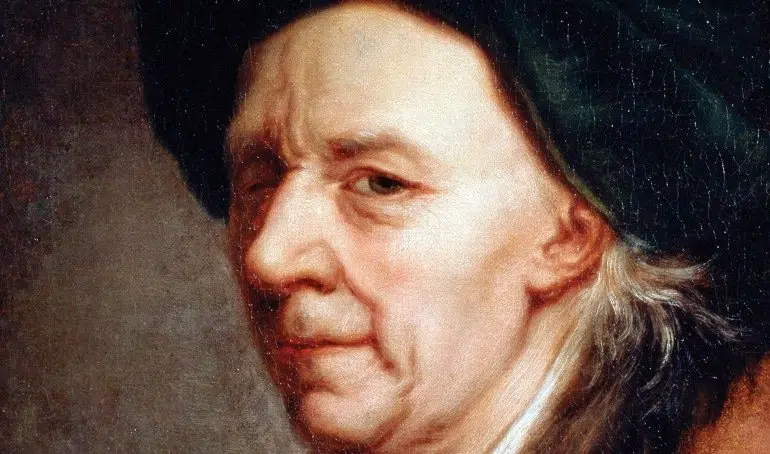

Leonhard Euler was a Swiss mathematician who lived from 1707 to 1783. He is extensively regarded as one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, having made significant contributions to various fields such as calculus, number theory, and graph theory.
Euler’s work in calculus was particularly revolutionary.
He introduced the concept of a function and developed many of the techniques that are still used today, including the use of logarithms and exponential functions.
He also made important contributions to the study of infinite series and differential equations.
In addition to his work in calculus, Euler also made big contributions to number theory.
He developed a formula for finding prime numbers and made important discoveries related to the theory of partitions and the distribution of prime numbers.
Euler’s work in graph theory was also very important. He introduced the concept of a graph and developed many of the techniques that are still used today, including the use of matrices to represent graphs.
Interesting fact: Euler was blind in his later years but continued to work on mathematics by dictating to his students.
Carl Friedrich Gauss: The Prince of Mathematicians
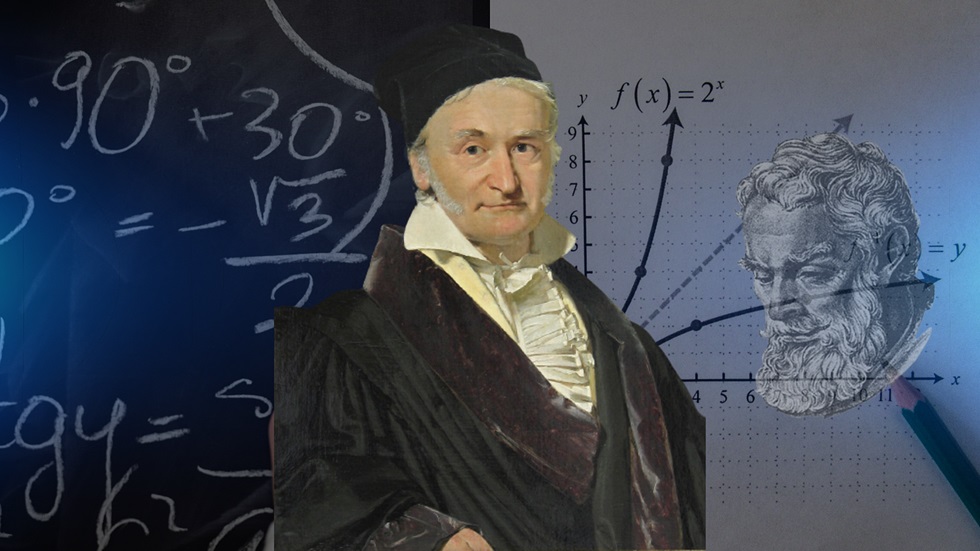

Carl Friedrich Gauss, born in 1777 in Brunswick, Germany, is certainly one of the greatest mathematicians of all time.
He made big contributions to a wide range of fields including number theory, algebra, statistics, and astronomy.
Gauss’s work has had a deep impact on modern mathematics and science.
One of Gauss’s most famous achievements is his discovery of the method of least squares. This method is used to find the line of best fit for a set of data and is still widely used today in fields such as statistics, engineering, and finance.
Gauss also made big contributions to number theory, including the discovery of the law of quadratic reciprocity and the development of modular arithmetic.
Gauss was a prolific mathematician and published numerous papers throughout his career.
Some of his most famous works include “Disquisitiones Arithmeticae,” and “Theoria Motus Corporum Coelestium.”
Interesting fact: Gauss was known for his mental arithmetic abilities and was able to perform complex calculations in his head at a young age.
Henri Poincaré: The Last Universalist

Henri Poincaré was a French mathematician who had great impact to various fields of mathematics, including topology, celestial mechanics, and algebraic geometry.
He is often considered the last universalist, as he was one of the last mathematicians who was able to make big contributions to a wide range of mathematical fields.
One of Poincaré’s most significant contributions was his work on the three-body problem in celestial mechanics.
He was the first to show that this problem does not have a general solution that can be expressed in terms of elementary functions.
This work laid the foundation for chaos theory, which is now a significant field of study in mathematics and physics.
Poincaré also made big contributions to algebraic topology, including the development of the fundamental group and the Poincaré conjecture. The Poincaré conjecture, which was finally proven in 2003 by Grigori Perelman, states that any compact, simply connected three-dimensional manifold is homeomorphic to the three-sphere.
Interesting fact: Poincaré was a prolific writer and published over 500 papers and several books throughout his career. He was also an influential philosopher of science and made contributions to the understanding of scientific methodology.
David Hilbert: The Axiomatic Method Pioneer
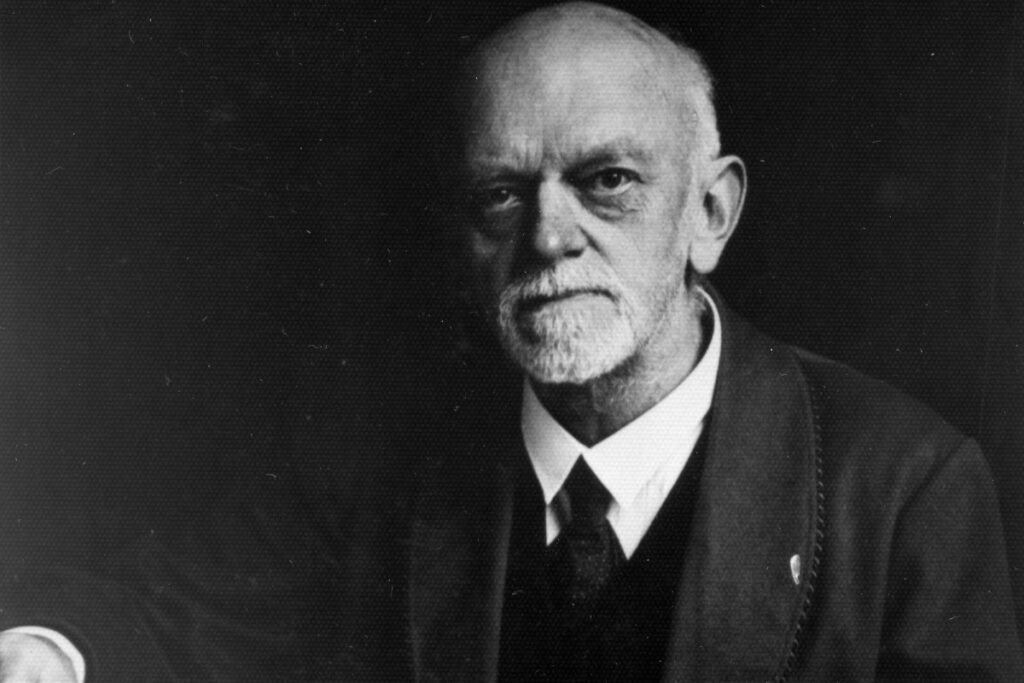

David Hilbert was a German mathematician who is known as one of the most influential mathematicians of the 19th and 20th centuries.
He was born in 1862 in Königsberg, Prussia (now Kaliningrad, Russia), where he spent most of his early life.
Hilbert is best known for his work on the foundations of mathematics, particularly his development of the axiomatic method. This method involves the use of a set of axioms or basic assumptions from which all other mathematical statements can be derived.
Hilbert believed that this approach would provide a solid foundation for all of mathematics, and he spent much of his career working to develop and refine it.
In addition to his work on the axiomatic method, Hilbert made significant contributions to a wide range of mathematical fields, including algebraic geometry, number theory, and mathematical physics.
He also played an important role in the development of the theory of relativity, working closely with Albert Einstein.
Interesting fact: David Hilbert is credited with the famous quote, "We must know, we will know," which has become a motto for many mathematicians.
Srinivasa Ramanujan: The Self-Taught Genius

Srinivasa Ramanujan was an Indian mathematician born in 1887. He is considered as one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, despite having no formal training in mathematics.
Ramanujan’s work was largely self-taught, and he made big contributions to several areas of mathematics, including number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions.
Ramanujan’s early life was marked by poverty and illness, but he showed a natural aptitude for mathematics from a young age.
He began to develop his own mathematical ideas as a teenager, and by the time he was in his early twenties, he had produced a large body of work that attracted the attention of mathematicians around the world.
One of Ramanujan’s most famous contributions to mathematics was his work on the partition function, which counts the number of ways that a given integer can be expressed as a sum of other integers.
Ramanujan developed a number of formulas and identities related to the partition function, many of which are still used today in various areas of mathematics and physics.
Interesting fact: Ramanujan claimed that his mathematical ideas came to him in dreams, and that he was visited by a goddess who gave him insights into mathematical truths. While this claim is difficult to verify, it is clear that Ramanujan had an extraordinary ability to see patterns and relationships in numbers that most other mathematicians could not.
Alan Turing: The Father of Theoretical Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence
Alan Turing is considered to be the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence due to his pioneering work on the concept of a universal machine, which is now known as the Turing machine.
Turing’s work on the Turing machine laid the foundation for the development of modern computers.
The Turing machine is a theoretical device that can simulate any computer algorithm, no matter how complex.
This idea led to the development of the first electronic computers, which were used to crack German codes during World War II.
In addition to his work on the Turing machine, Turing also made significant contributions to the field of artificial intelligence.
He proposed the Turing test, which is still used today to determine whether a machine can exhibit intelligent behavior that is indistinguishable from that of a human.
Interesting fact: Alan Turing was posthumously pardoned by the British government in 2013 for his conviction of homosexuality in 1952, which was then considered a criminal offense.
Terence Tao: Modern Genius
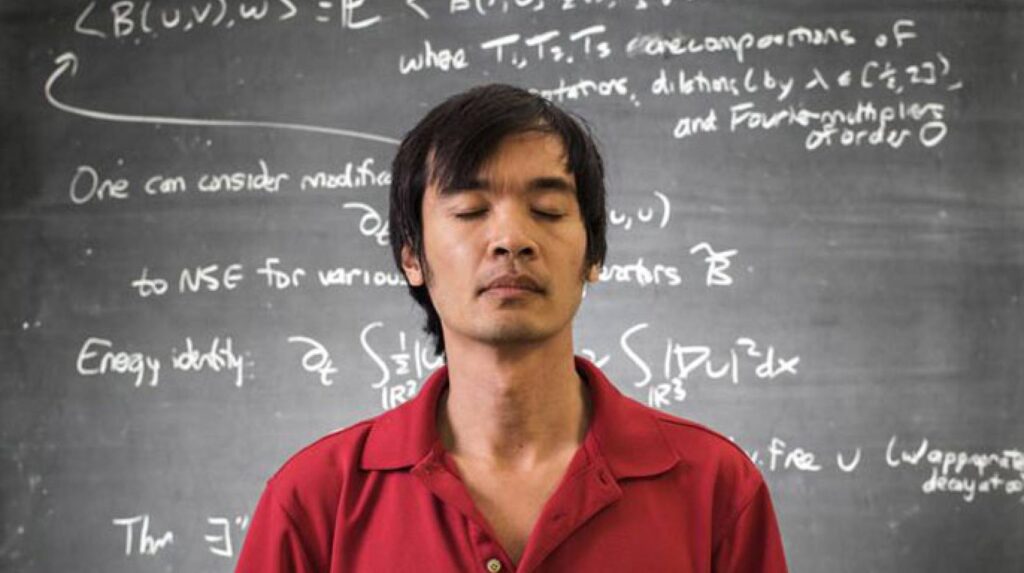

Terence Tao is a contemporary mathematician who has already made a great impact in the field of mathematics.
Born in Adelaide, Australia in 1975, Tao was a child prodigy who began taking university-level mathematics courses at the age of nine.
He received his Ph.D. from Princeton University at the age of 21, and has since become one of the most influential mathematicians of our time.
Tao’s research interests include number theory, harmonic analysis, and partial differential equations. He has made innovative contributions to each of these fields, and has received numerous awards and honors for his work.
In 2006, he was awarded the Fields Medal, which is seen as the highest honor in mathematics.
In addition to his research, Tao is also a prolific writer and educator.
He has authored or co-authored more than 300 research papers and several books, and has taught at several universities around the world. He is currently a professor of mathematics at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Interesting fact: Tao was a child prodigy who began taking university-level mathematics courses at the age of nine. Terence Tao’s IQ is 230 which makes him officially the smartest person alive per intelligence quotient (IQ) tests.




















