
Physics is a branch of science that fascinates us, makes us wonder, and enables us to understand how our world and reality work.
New findings in physics are very rare, especially in recent times, but when they happen, it is something extraordinary—something with the potential to change how we understand the world around us and to comprehend mysteries of the universe, such as black holes or dark matter.
For the common people, advanced physics, like quantum field theory, is completely incomprehensible, yet it serves as a playground for some genius people.
Those kinds of people will be on this list.
This article will highlight the top 10 greatest physicists of all time. These individuals have made substantial contributions to the field of physics, and their work has had a lasting impact on our understanding of the world and the entire universe.
From the theory of relativity to quantum mechanics, these physicists have made innovative discoveries that have shaped the course of modern physics.
So, let’s start with the list.
Let’s entangle together with those genius minds…
Isaac Newton
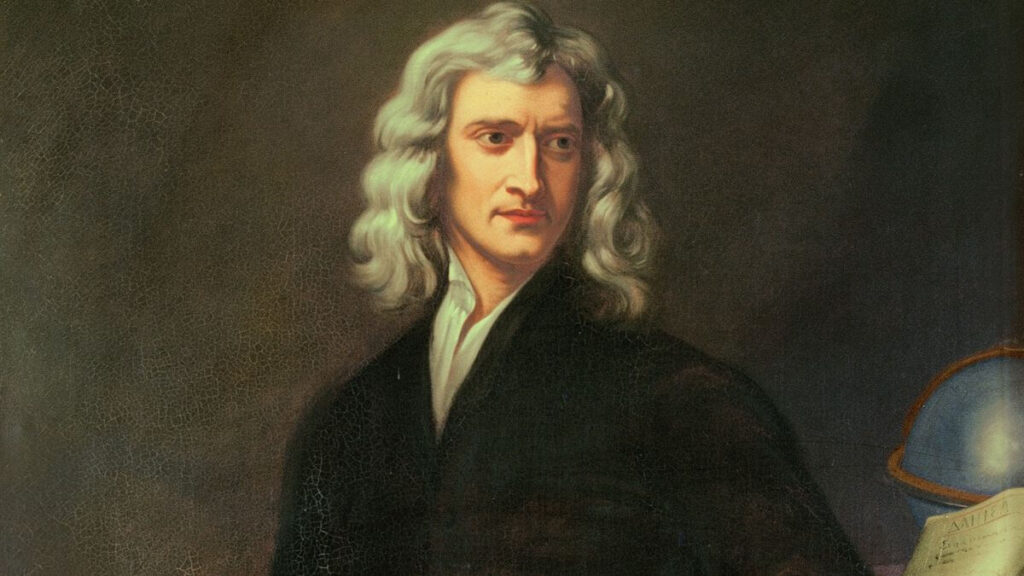

Isaac Newton is widely considered to be one of the greatest physicists of all time. He was born on January 4, 1643, in Woolsthorpe, England. Newton made huge contributions to the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy.
One of Newton’s most famous contributions is his laws of motion, which describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting upon it. These laws are still used today in the study of physics and engineering.
Newton also developed the theory of universal gravitation, which explains how all objects in the universe are attracted to each other. This theory was a major breakthrough in the understanding of the laws that govern the motion of celestial bodies.
In addition to his scientific contributions, Newton was also a skilled mathematician. He is credited with developing calculus, a branch of mathematics that is used in physics and engineering.
Interesting fact: Newton was a member of the Royal Society, a prestigious organization dedicated to the advancement of science. He was elected as the society's president in 1703 and served in that position until his death in 1727.
Recommendation: If you’re rather interested in Newton’s fascinating life, we highly recommend the following book: “Isaac Newton”, by James Gleick.
Albert Einstein
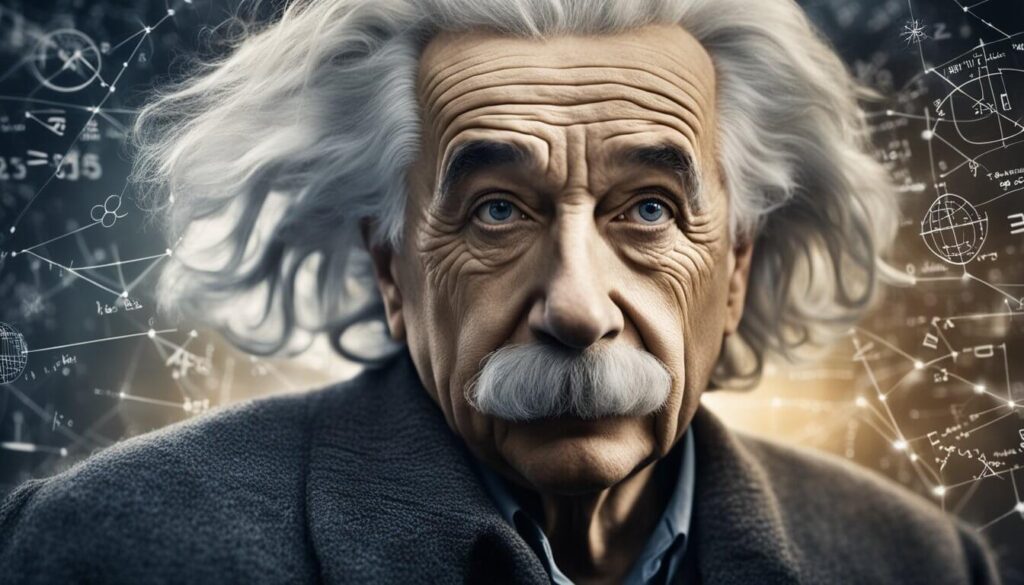

Albert Einstein is certainly the most famous one on this list. Probably there isn’t a person in the world who hasn’t heard of Einstein. He is best known for his theory of relativity, which revolutionized the way we think about space and time.
Einstein’s work on relativity led to a number of important discoveries, including the famous equation E=mc², which shows the relationship between mass and energy.
He also made significant contributions to the development of quantum mechanics, and his work on the photoelectric effect earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
In addition to his scientific work, Einstein was also a vocal advocate for peace and social justice. He was a pacifist who opposed war and nuclear weapons, and he spoke out against racism and discrimination.
Interesting fact: Einstein was offered the presidency of Israel in 1952, but he declined the offer, saying that he did not have the necessary experience or qualifications.
Recommendation: There are many books about Einstein out there, but we would like to recommend the book that he wrote himself. "The World as I See It" is his collection of essays and reflections about the world and humanity. In this book, Einstein is deeply concerned about humanity in many different categories, from war and education to social injustice and nationalism.
Niels Bohr
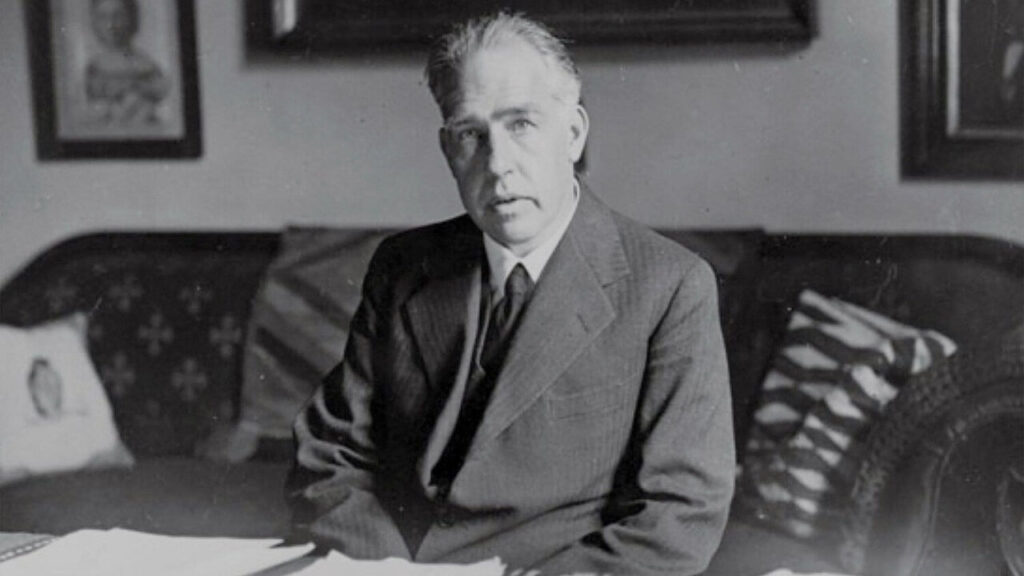

Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who made very important contributions to the field of quantum mechanics and atomic structure. He is best known for his model of the atom, which is still widely used today.
Bohr proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels and that the emission or absorption of energy by an atom occurs when an electron moves from one energy level to another. This model helped to explain the periodic table and the behavior of atoms in chemical reactions.
In addition to his work on atomic structure, Bohr also made important contributions to the development of nuclear physics. He was instrumental in the discovery of nuclear fission and helped to establish the first nuclear reactor.
Interesting fact: Bohr was a member of the Danish resistance during World War II and helped to smuggle Jewish scientists out of Nazi-occupied Europe.
Recommendation: If you'd like to find out more about Niels Bohr's life, this is the book to go to: "Niels Bohr's Times, In Physics, Philosophy, and Polity."
Werner Heisenberg
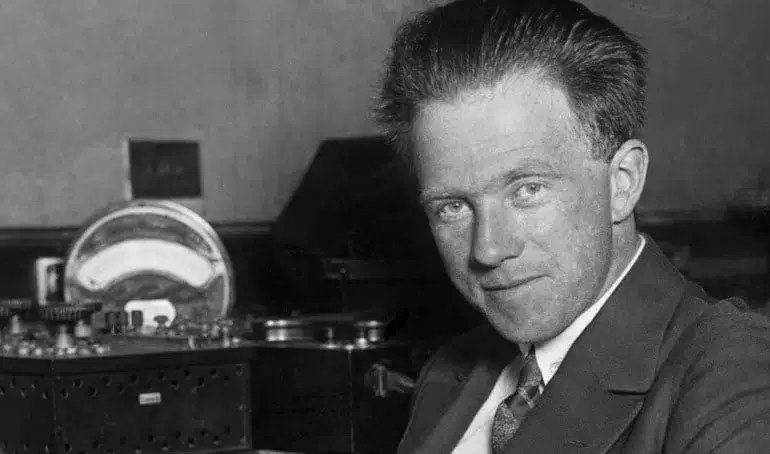

Werner Heisenberg was a German physicist who is best known for his contributions to quantum mechanics. He was born on December 5, 1901, in Würzburg, Germany. Heisenberg received his doctorate in physics from the University of Munich in 1923. He then worked as an assistant to Max Born at the University of Göttingen and later as a professor at the University of Leipzig.
Heisenberg’s most famous contribution to physics is the uncertainty principle, which he formulated in 1927. The uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously measure the position and momentum of a particle with absolute accuracy. This principle revolutionized the way physicists think about the behavior of subatomic particles.
In addition to his work on quantum mechanics, Heisenberg also made important contributions to nuclear physics. During World War II, he worked on the German nuclear energy project, which aimed to develop an atomic bomb. After the war, he was briefly held as a prisoner of war by the Allies.
Interesting fact: Heisenberg was a talented pianist and often played music to relax after working on physics problems.
Recommendation: “Encounters with Einstein" is a collection of essays written by Werner Heisenberg himself. This is one of the most fluent books about modern physics; however, it is rarely mentioned in today’s times.
Erwin Schrödinger

Erwin Schrödinger was an Austrian physicist who is known for his big contributions to quantum mechanics. He was born in Vienna in 1887 and received his education in physics at the University of Vienna. In 1926, he published his famous paper on wave mechanics, which introduced the Schrödinger equation that describes the behavior of quantum particles.
Schrödinger’s work on wave mechanics was groundbreaking and helped to establish the foundations of quantum mechanics. He also made important contributions to the theory of color vision and the theory of entropy. In addition to his work in physics, Schrödinger was also interested in philosophy and wrote extensively on the subject.
Interesting fact: Schrödinger is perhaps best known for his famous thought experiment, known as Schrödinger's cat, which illustrates the paradoxical nature of quantum mechanics. In simple terms Schrödinger's cat is a thought experiment describing the idea in quantum physics that something can exist in two states at once, like a cat being both alive and dead until someone checks.
Recommendation: If you're interested about mind-bending connections between physics and biology, you will be rather happy with this book: "What is Life?" by Erwin Schrödinger. Published in 1944, it dives into how living things keep their act together and even foreshadows DNA discoveries. It's a must-read for anyone curious about the essence of life!
James Clerk Maxwell

James Clerk Maxwell was a Scottish physicist who lived from 1831 to 1879. He is considered to be one of the greatest physicists of all time due to his contributions to the field of electromagnetism.
Maxwell developed a set of equations known as Maxwell’s equations, which describe the behavior of electric and magnetic fields. These equations are still widely used today and have been instrumental in the development of modern technology, including radio and television.
In addition to his work in electromagnetism, Maxwell also made significant contributions to the study of optics and thermodynamics. He was the first person to demonstrate the color photograph process, and he developed a theory of gases that helped explain the behavior of molecules.
Interesting fact: Maxwell was known for his sense of humor and enjoyed playing practical jokes on his colleagues. He once sent a letter to a friend written entirely in code, which took the friend several days to decipher.
Recommendation: One of the best biographies about scientists is certainly: “The Man Who Changed Everything: The Life of James Clerk Maxwell.” It is basically biography of a founder of modern scientific thought, and could not recommend it more.
Paul Dirac
Paul Dirac was a British theoretical physicist who was born on August 8, 1902, in Bristol, England. He is known for his contributions to quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics. Dirac was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933, jointly with Erwin Schrödinger, for their contributions to the development of atomic theory.
Dirac was the first to propose the existence of antimatter, which was later confirmed by experiments. He also introduced the concept of the Dirac equation, which describes the behavior of relativistic particles. Dirac’s work on quantum electrodynamics was instrumental in the development of the theory of quantum field theory.
Interesting fact: Dirac was known for his reserved personality and his ability to solve complex mathematical problems in his head without the need for pen and paper.
Recommendation: If Paul Dirac's story interests you, we suggest checking out "The Strangest Man: The Hidden Life of Paul Dirac." This book uncovers the fascinating life and contributions of Dirac to quantum physics, making it a great read for those curious about his journey and impact on the scientific world.
Michael Faraday

Michael Faraday was an English physicist and chemist who made important contributions to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. He was born on September 22, 1791, in Newington Butts, England, and died on August 25, 1867, in Hampton Court, England.
Faraday’s most significant contribution was his discovery of electromagnetic induction, which laid the foundation for the development of the electric generator. He also discovered benzene and made noteworthy contributions to the understanding of electrolysis.
Faraday was mostly self-taught scientist who started his scientific career as an apprentice to a bookbinder. He attended lectures by the famous chemist Humphry Davy and eventually became his assistant.
Interesting fact: Faraday was offered a knighthood by Queen Victoria, but he declined the honor.
Recommendation: The book "Michael Faraday: Father of Electronics" by Charles Ludwig paints a remarkable story about Michael in semi-fictional form. A truly fluent and great read.
Marie Curie

Marie Curie was a Polish-born physicist who made revolutionary contributions to the field of radioactivity. She was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize and the first person to win two Nobel Prizes in different fields (chemistry & physics).
Curie’s research on radioactivity led to the discovery of two new elements, polonium and radium. She also developed methods for isolating radioactive isotopes and used them to treat cancer patients.
Despite facing discrimination as a woman in the male-dominated field of science, Curie persevered and made significant contributions to many fields.
Interesting fact: Marie Curie's notebooks are still highly radioactive and must be kept in lead-lined boxes to prevent radiation exposure.
Recommendation: Probably the best book about Marie is "Madame Curie: A Biography," written by her daughter, Eve Curie. It’s a particularly interesting book about the astonishing and genius mind of Marie Curie.
Richard Feynman

Richard Feynman was an American theoretical physicist who is widely regarded as one of the most influential physicists of the 20th century. He was born on May 11, 1918, in New York City and died on February 15, 1988, in Los Angeles, California.
Feynman made weighty contributions to the development of the atomic bomb during World War II. He also developed the theory of quantum electrodynamics, which describes the behavior of light and matter at the atomic and subatomic level. Feynman received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 for his work on quantum electrodynamics.
In addition to his scientific work, Feynman was known for his engaging and humorous lectures. He authored several books, including “Surely You’re Joking, Mr. Feynman!” and “The Feynman Lectures on Physics.”
Interesting fact: Feynman was a skilled bongo player and often played in samba bands.
Note: If you enjoyed this article you might also like:




















