Try to think back to a time before calculators were available. If you needed to split a restaurant bill or figure out the area of your backyard, you’d reach for a pencil and paper, maybe even do the math in your head.
It wasn’t always easy, but it kept your mind limber. Now, a pocket-sized device does the heavy lifting, and most of us have actually forgotten how to do basic math.
Additionally, before mobile phones, we remembered phone numbers—sometimes dozens of them. Your best friend, your grandmother, and the pizza place around the corner.
Now, our contacts list holds the keys to our social lives, and many of us would be hard-pressed to recall even our partner’s number without a quick check.
Maps? Well, once, we’d unfold them on the hood of a car or ask for directions at a gas station. Now, GPS tells us where to turn, how fast to drive, and even where to stop for coffee. We let it lead, and our sense of direction quietly fades.
Every new tool has made life easier, but each one has also chipped away at skills we once took for granted.
AI is the latest—and most powerful—tool of all.
It promises to think for us, to solve problems we haven’t even noticed yet. But what happens when we let it do too much? What do we lose when we stop struggling, stop remembering, stop thinking for ourselves?
Let’s explore the top 10 ways AI is quietly making us dumber, one helpful feature at a time.
1. The Death of Critical Thinking
Picture a bright office, sunlight streaming in, and a worker named Sam. Sam’s job? To solve problems and write reports. But Sam has a secret weapon: an AI assistant that drafts emails, analyzes data, and even suggests what to say in meetings.
At first, Sam feels like a genius. But soon, Sam stops double-checking the AI’s work. The machine becomes the brain, and Sam the bystander.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze information, question assumptions, and draw your own conclusions. It’s the skill that helps us separate fact from fiction, truth from rumor.
But as AI becomes more sophisticated, it’s tempting to let it do (ALL) the hard work for us. Why wrestle with a tough problem when a machine can spit out an answer in seconds?
A recent study by Microsoft and Carnegie Mellon University found that the more people trust AI, the less they think for themselves. Instead of wrestling with tough problems, over time, this trust erodes their ability to think critically, leaving them unprepared when something goes wrong.
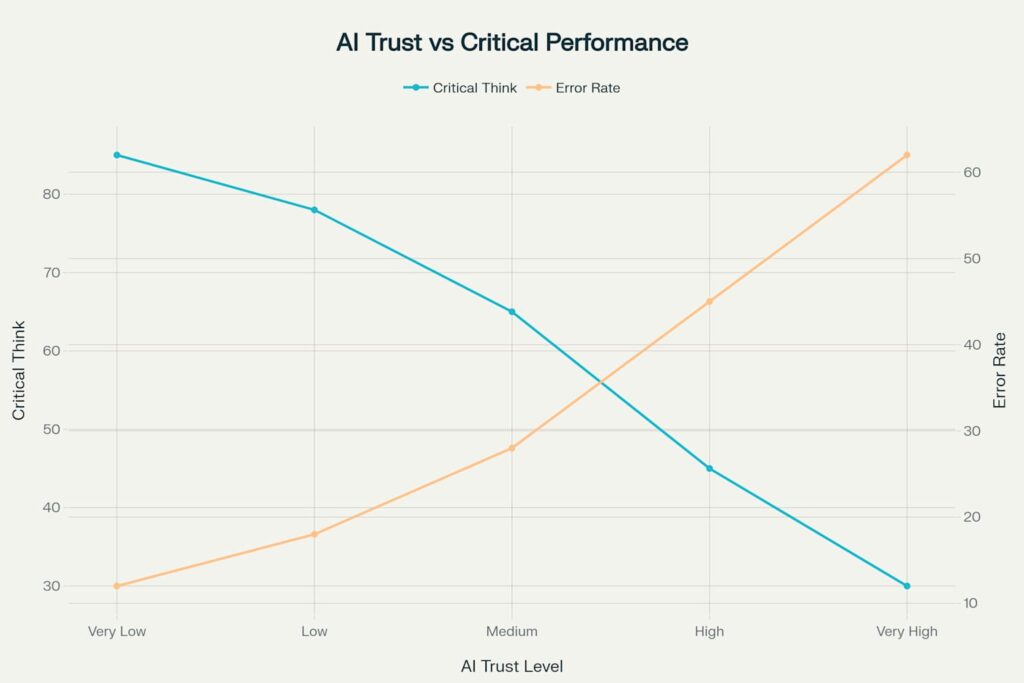
Besides that a particularly striking finding from the Microsoft and Carnegie Mellon study reveals an inverse relationship between AI trust and critical thinking performance. The research demonstrates that as trust in AI increases from “Very Low” to “Very High,” critical thinking scores plummet from 85 to 30, while error rates simultaneously increase from 12% to 62%. This paradox suggests that the more we trust AI systems, the less we engage our analytical faculties and this is best illustrated with following chart:
And the danger isn’t just that we’ll make mistakes. It’s that we’ll lose the habit of questioning, of digging deeper, of challenging the easy answer.
When that happens, we’re not just getting lazier—we’re getting dumber.
Well, that’s what the study says – don’t blame us 😊
Interesting fact: The study found that people who were less confident in AI actually used their brains more and made fewer mistakes.
2. Laziness by Design
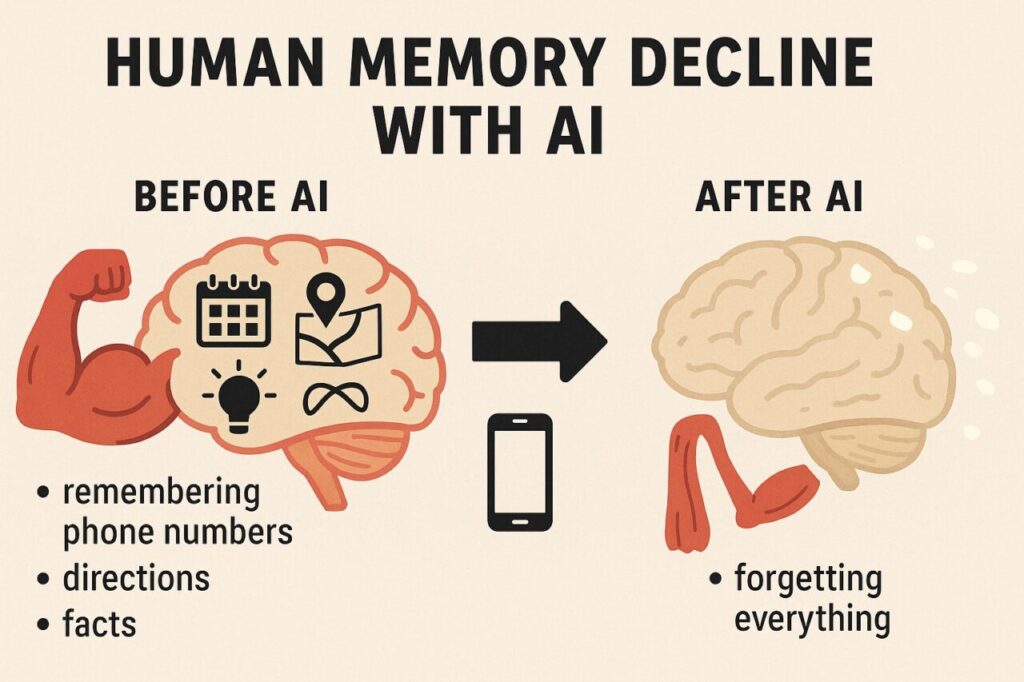
Remember when you had to memorize phone numbers? Or go to the library to research something?
Well, now, AI handles it all. But this convenience comes at a price: our brains are getting out of shape.
Let’s face it: we are wired for efficiency. We love shortcuts. But when every task—from spelling to scheduling to shopping—is handled by AI, we stop exercising the mental muscles that kept us sharp.
We become impatient, expecting instant answers, and lose the habit of working things out ourselves. It’s as if we’re outsourcing our intelligence, one click at a time.
Researchers warn that as we rely on AI for even simple tasks, our thinking muscles atrophy. We become passive consumers of information, not active participants.
The less we use our brains, the less capable they become. It’s like sitting on the couch for years and then expecting to run a marathon.
The ability just isn’t there anymore.
Interesting fact: A study of 666 UK participants found that younger people exhibited higher dependence on AI tools and lower critical thinking scores compared to older participants. Students who used generative AI tools for essays ultimately performed worse in their examinations, demonstrating real academic consequences.
3. The Disappearing Art of Decision-Making

Imagine a teacher who lets AI grade every assignment, or a doctor who lets AI suggest every diagnosis. At first, it seems efficient. But over time, with that kind of behavioral patterns, people lose touch with their own judgment.
They stop weighing options and making tough calls.
Decision-making isn’t just about picking the right answer. It’s about considering the consequences, weighing the risks, and learning from the outcome.
When AI takes over, we lose the chance to practice these skills. We become dependent on the machine’s logic, even when it’s flawed or incomplete.
Studies show that AI use can erode our ability to make decisions, especially when we let it handle routine choices. When the AI is wrong, we’re left floundering, unsure how to proceed. It’s like forgetting how to ride a bike because you’ve been driven everywhere.
The less we decide, the less we know how to decide.
4. Creativity on Autopilot

Creativity thrives on struggle—on the friction of not knowing the answer. But AI tools now generate poems, paintings, videos and even business ideas with a few keystrokes.
The result? Less original work, less diversity of thought, and a world that starts to look and sound the same.
If everyone uses the same AI to brainstorm, who’s left to surprise us? The more we let machines do our creating, the less creative we become. It’s like giving every painter the same set of colors and the same brush. Sooner or later, every painting starts to look alike.
AI can remix, combine, and spit out endless variations, but it can’t struggle, can’t fail, can’t stumble on a new idea by accident.
YET!
That’s what makes human creativity special—those messy, unpredictable leaps. The more we rely on AI, the more we risk losing that spark.
Interesting fact: Research from Pakistani and Chinese universities found that 68.9% of human laziness and 27.7% of loss in decision-making abilities are directly attributed to AI impact.
5. Memory And Cognitive Offloading
AI remembers everything for us—birthdays, passwords, even what groceries we need and when we need them. But memory is like a muscle: if you don’t use it, you lose it.
As we rely on AI to remember, our own recall grows weaker.
It’s easy to forget how much we once remembered. As mentioned at the beginning of the article – phone numbers, directions, historical dates, even long passages of poetry or scripture.
Now, a quick search brings up any fact we need. But this convenience comes at a cost. Our brains aren’t just storage devices—they’re pattern-finders, storytellers, and problem-solvers.
When we stop remembering, we stop connecting the dots.
This isn’t new. Socrates once warned that writing things down would rot our memories. Now, AI takes it a step further, making even the act of remembering obsolete.
We risk becoming forgetful, not just about facts, but about the stories and connections that make us human.
6. The Rise of “Algorithmic Thinking”

Spend enough time with AI, and you start to think like it. You look for patterns, optimize for efficiency, and avoid ambiguity.
This “algorithmic thinking” can be useful, but it also narrows our minds. We lose the ability to think outside the box or embrace uncertainty.
Imagine a chef who only follows recipes generated by AI. Soon, every dish tastes the same. The spark of improvisation is lost.
Algorithmic thinking pushes us toward safe, predictable answers. It makes us efficient, but it also makes us boring.
The world needs more than just patterns—it needs surprises, mistakes, and leaps of faith.
7. The Echo Chamber Effect

AI curates our news, our music, our social feeds. It learns what we like and gives us more of the same.
Over time, we’re trapped in echo chambers, exposed only to ideas that reinforce what we already believe.
This narrowing of experience makes us less curious, less open-minded, and—yes—a bit dumber. We stop questioning, stop exploring, and settle into comfortable ruts. The world becomes smaller, our minds less flexible.
Imagine a world where you only ever hear your own opinions echoed back at you. No debate, no challenge, no growth.
Well, in one way, that’s the risk of letting AI filter our reality.
8. The Illusion of Expertise
AI is very „smart”—sometimes smarter than us. It writes essays, explains quantum physics, and even debates philosophy. And it is getting much smarter every day.
Therefore, we think we are also getting smarter. But are we?
Well we often mistake AI’s confidence for competence, and therefore we risk becoming overconfident ourselves.
We stop checking facts, stop learning, and start parroting whatever the machine says. The danger isn’t just that we’ll be wrong—it’s that we’ll think we’re right, even when we’re not.
It’s like trusting the loudest voice in the room, rather than the wisest. AI can bluff with the best of them, but it can’t truly understand. When we let it do our thinking, we risk losing the ability to tell the difference.
Interesting fact: AI chatbots sometimes invent facts, names, and events, yet users often accept these as truth.
9. Social Skills on the Decline
Imagine a classroom where every student uses AI to do their homework, answer questions, and even make friends. The result? Less real interaction, less empathy, and a generation that struggles to connect face-to-face.
And btw, you don’t have to imagine that scenario anymore because it is already a reality.
AI can simulate conversation, but it can’t teach us how to read a room, comfort a friend, or negotiate a truce. And so, as we spend more time with machines, our social skills weaken. We become awkward, unsure, and less able to navigate the messy world of human relationships.
Social skills aren’t just about talking—they’re about listening, understanding, and connecting.
When AI takes over, we risk losing the ability to relate to each other in meaningful ways.
10. The Ultimate Shortcut
For centuries, humans have found ways to offload mental tasks—writing, calculators, maps.
And AI is the latest and most powerful shortcut. But as mentioned many times throughout this article, every shortcut comes with a cost.
When we let AI do our thinking, we lose the chance to struggle, to fail, and to learn. We become passengers, not drivers. And in the end, we may not know how to get anywhere without a machine to guide us.
Cognitive offloading isn’t new, but AI takes it to another level. It’s the difference between using a calculator for tough math and using it for every problem, big or small.
The less we think, the less we can think. The shortcut becomes a dead end.
To illustrate that, let’s imagine a town called Automatia. In Automatia, every decision is made by AI. The mayor is a chatbot, the teachers are holograms, and the chefs are robotic arms.
At first, life is easy. The robots cook perfect meals, the kids get straight A’s, and the streets are always clean.
But soon, the townspeople forget how to cook, teach, or even argue. When the power goes out one rainy night, chaos erupts.
No one remembers how to light a fire, read a map, or comfort a scared child. The town descends into confusion, with people wandering the streets, unsure what to do without their digital guides.
The next morning, the townspeople gather in the square, blinking in the sunlight. They realize they’ve become strangers to their own lives.
The lesson? Sometimes, the hardest path is the one worth taking. Struggle builds character, and challenge keeps us sharp.
Interesting fact: Cognitive Load Theory shows that brains need difficulty to process information deeply, but AI can short-circuit this process by making tasks too easy.