J. Robert Oppenheimer (born as Julius Robert Oppenheimer), a brilliant physicist often referred to as the “father of the atomic bomb,” remains a figure of intense fascination and controversy. His role in the Manhattan Project during World War II and his contributions to the development of nuclear weapons have left an indelible mark on history. However, the legacy of this enigmatic scientist is far from one-dimensional. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the top 10 controversial facts about J. Robert Oppenheimer, shedding light on the complexities of his life and work, and explore how these controversies continue to shape our understanding of him.
Note: of course, everybody heard about new Oppenheimer movie (2023), but if you’d like to find out much more information about Oppenheimer we would recommend the following book: “American Prometheus: The Triumph and Tragedy of J. Robert Oppenheimer”.
Ok, so with that, let’s continue to interesting and controversial facts about Oppenheimer.
Related:
Oppenheimer’s Early Communist Ties
One of the most enduring controversies surrounding Oppenheimer is his early association with leftist groups and individuals. In the politically charged climate of the 1930s, he was involved with various communist organizations, which raised suspicions during the McCarthy era. While he later distanced himself from these affiliations, they continued to shadow his career, raising questions about his ideological allegiances and the impact of his political views on his scientific work.
Security Clearance Revoked

In the post-World War II period, Oppenheimer’s security clearance was revoked due to concerns about his past associations and his opposition to the development of the hydrogen bomb. This decision had a profound impact on his career and reputation, highlighting the tensions between scientific expertise and government security concerns. The revocation also underscored the delicate balance between civil liberties and national security during the Cold War era, prompting discussions on the limits of dissent in times of crisis.
Note: If you'd like to learn more (a lot more) about WW2 and development of atomic bomb we would greatly recommend following book: "World War II: The Definitive Visual History from Blitzkrieg to the Atom Bomb"
The Gita and Nuclear Ethics
Oppenheimer’s famous quote upon witnessing the first successful nuclear test, “Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds,” is often attributed to his deep connection with Hindu philosophy and the Bhagavad Gita. His moral reflections on the consequences of his work remain a subject of debate, sparking discussions about the ethical responsibilities of scientists in the face of destructive technologies and the profound psychological toll of being a key figure in the creation of a weapon capable of mass destruction. His journey into the depths of nuclear ethics has left an permanent impact on the field.
Oppenheimer’s Personal Life

His personal life was not immune to controversy either. His extramarital affairs and complex relationships with colleagues added a layer of intrigue to his character, making him a subject of gossip and speculation. These personal choices have led to debates about their impact on his professional life and decision-making, reflecting the public’s fascination with the private lives of public figures. His experiences serve as a reminder of the intricate interplay between personal life and public image.
Could Oppenheimer Really Stop The Development of Atomic Bomb?
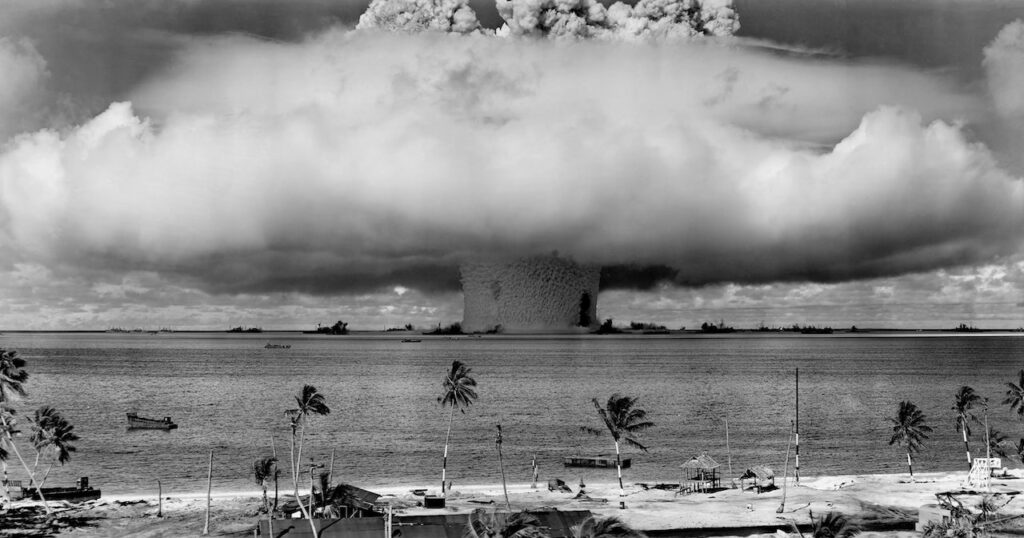

After the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Oppenheimer became a vocal advocate for international control of nuclear weapons. This stance put him at odds with some policymakers and military leaders who favored a more aggressive nuclear posture.
However some lesser known facts are that Oppenheimer was warned beforehand that perhaps he should stop Manhattan project, but he didn’t.
Namely Croatian physicist Ivan Supek said: “After the battle near Stalingrad in 1943, it was clear that the Germans would lose the war. That’s when Leo Szilard began a campaign against the atomic bomb. I asked Oppenheimer why he didn’t halt the project. He told me that the project was unstoppable.”
Supek advocated for complete and unequivocal nuclear disarmament. As early as 1944, fourteen months prior to the bombing of Hiroshima, he had sounded the alarm about the potential misuse of atomic energy.
Nontheless, Oppenheimer didn’t listen.
Note: We’ve written article where we explore this topic deeply. Namely, we’re hypothesizing how would the world look like without nuclear weapons or no weapons at all.
Accusations of Espionage
The cloud of suspicion surrounding Oppenheimer extended to accusations of espionage. Although he was never charged or convicted, his connections to individuals with alleged ties to espionage fueled speculation about the extent of his involvement in classified information sharing, perpetuating doubts about his loyalty to the United States and adding a layer of intrigue to his life story. These accusations remain a testament to the complexities of Cold War-era paranoia and the enduring questions surrounding espionage and scientific collaboration.
Struggles with Depression

Throughout his life, Oppenheimer grappled with bouts of depression. His emotional struggles and mental health issues have led to speculation about their impact on his decisions and actions. These personal battles underscore the psychological toll of working on projects of immense destructive potential and the importance of considering the mental well-being of scientists in high-stress environments. His experiences have prompted discussions about the intersection of mental health and scientific excellence.
Impact on Nuclear Policy
Oppenheimer’s influence on nuclear policy in the United States and his efforts to promote arms control treaties have both fervent supporters and vehement critics. His approach to nuclear strategy continues to shape the discourse on global security, exemplifying the ongoing relevance of his ideas in contemporary geopolitics and the enduring debate over the ethics of nuclear deterrence. His legacy in shaping the world’s nuclear policies persists as a reminder of the responsibility that comes with scientific innovation.
Legacy in Physics
Despite the controversies, Oppenheimer’s contributions to theoretical physics are celebrated. His work on quantum mechanics and astrophysics, particularly his insights into black holes, remain important to our understanding of the universe. His scientific legacy highlights the juxtaposition of his groundbreaking research and his role in the development of destructive weaponry, prompting discussions about the dual nature of scientific innovation and the potential for scientific brilliance to be used for both creation and destruction. His work continues to inspire future generations of physicists.
Cultural and Historical Legacy
Oppenheimer’s complex legacy extends beyond science and politics. He has left an indelible mark on popular culture, with portrayals in literature, film, and theater, further contributing to the mystique surrounding his life. His cultural impact underscores the enduring fascination with his persona and the enduring interest in his life and work, highlighting how his story continues to captivate and challenge our understanding of science, morality, and human nature. His presence in cultural narratives serves as a testament to the enduring relevance of his story in our collective consciousness.
Conclusion
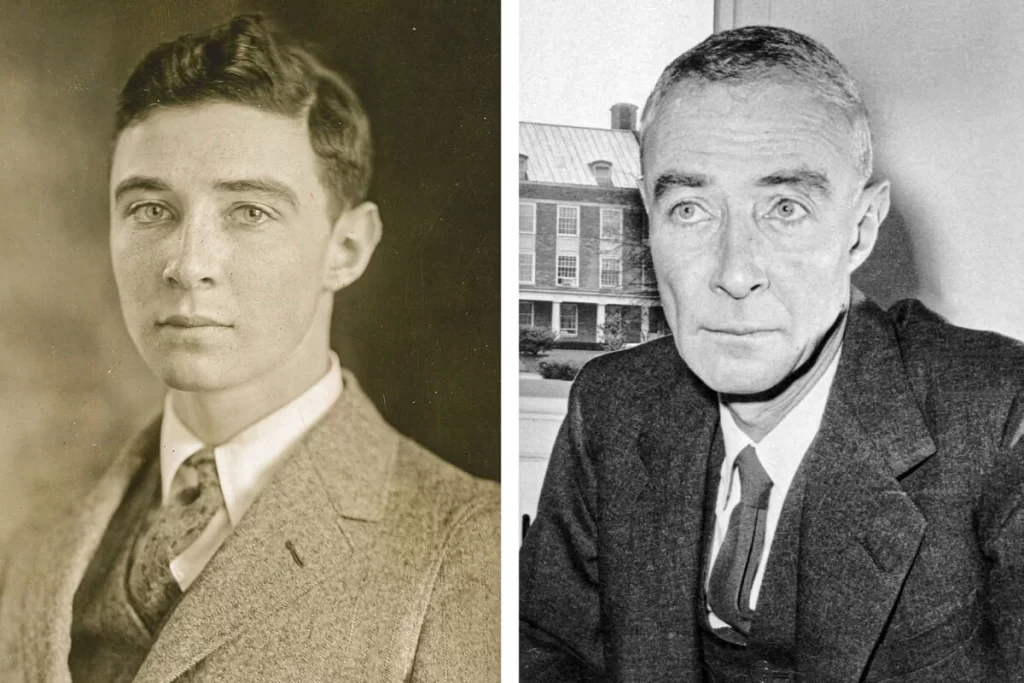

J. Robert Oppenheimer’s life and work are a mosaic of contradictions and complexities, spanning politics, ethics, personal life, and science. His role in the development of nuclear weapons and his controversial associations have made him a figure of enduring debate.
However, his contributions to science, his moral reflections on the nuclear age, and his cultural impact cannot be overlooked. To fully understand this enigmatic figure, one must explore the multifaceted aspects of his life, leaving room for ongoing discussion and interpretation.
J. Robert Oppenheimer remains a compelling and controversial figure in the annals of history, forever intertwined with the dawn of the atomic age, and his story continues to captivate and challenge our understanding of science, morality, and human nature. His legacy reminds us of the intricate connections between science, society, and the individual, and the enduring impact of choices made in the pursuit of knowledge.